Nvidia's Ultra, Rubin, and Feynman: A Data Center Revolution?
Nvidia's recent announcements surrounding the Grace Hopper Superchip (codenamed "Hopper"), the Grace CPU, and the upcoming "Rubin" and "Feynman" processors are generating significant buzz within the tech industry. These advancements promise a potential revolution in data center architecture and performance, pushing the boundaries of AI, high-performance computing (HPC), and cloud computing. But are these claims justified, and what does this mean for the future of data centers? Let's delve deeper.
The Hopper Architecture: A Giant Leap for AI
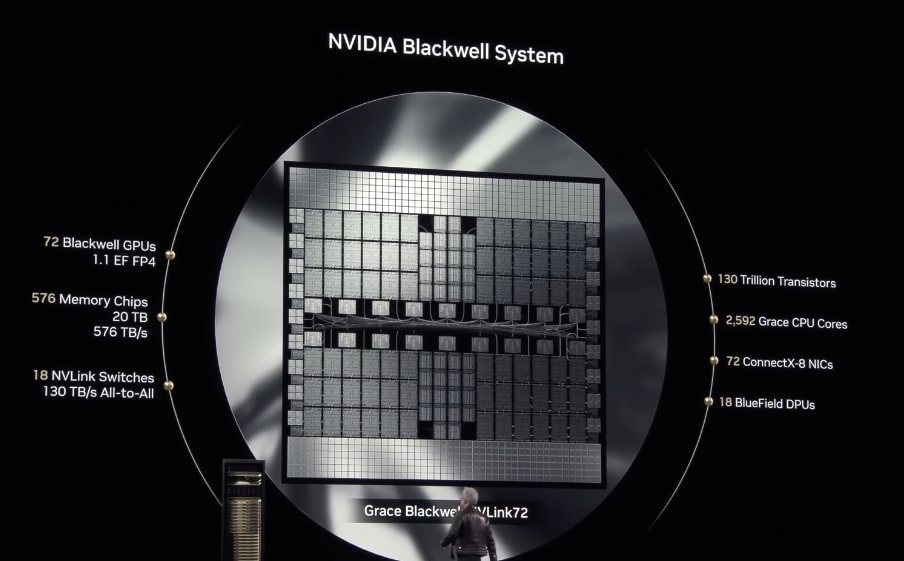
The Grace Hopper Superchip, built on Nvidia's Hopper architecture, is a game-changer. This system combines the power of the Grace CPU with the unparalleled performance of the Hopper GPU, creating a cohesive system optimized for data-intensive workloads. Key features include:
- Unified Memory: This innovative architecture allows the CPU and GPU to share memory directly, eliminating bottlenecks and dramatically speeding up data transfer. This is crucial for AI model training and inference.
- High Bandwidth Interconnect: The NVLink C2C interconnect provides blazing-fast communication between the CPU and GPU, further enhancing performance.
- Improved AI Performance: The Hopper architecture boasts significant improvements in AI processing capabilities, making it ideal for large language models (LLMs) and other demanding AI applications.
The implications for data centers are vast. This technology significantly accelerates AI model training, allowing for faster development and deployment of innovative AI solutions. Expect to see Hopper-powered systems powering everything from autonomous vehicles to advanced medical research.
Grace CPU: A Powerhouse for HPC
Nvidia's foray into the CPU market with the Grace CPU isn't just a side project; it's a strategic move to build a complete, optimized system. Designed specifically to work seamlessly with the Hopper GPU, the Grace CPU offers:
- High Core Count: The Grace CPU boasts a large number of cores, optimized for parallel processing and demanding HPC workloads.
- High Memory Bandwidth: Similar to the Hopper Superchip, the Grace CPU offers high memory bandwidth, crucial for handling massive datasets.
- Enhanced Interconnectivity: The Grace CPU is engineered for efficient communication with other Grace CPUs and Hopper GPUs within a system.
This leads to significant improvements in HPC applications, including weather forecasting, scientific simulations, and drug discovery. Data centers will benefit from the increased efficiency and speed provided by this specialized CPU architecture.
The Enigma of Rubin and Feynman: Future Data Center Powerhouses?
While details remain scarce, rumors surrounding the "Rubin" and "Feynman" processors suggest even more substantial advancements in data center technology. These next-generation processors are expected to build upon the successes of Hopper and Grace, potentially incorporating:
- Advanced Packaging Technologies: Expect to see more sophisticated packaging techniques to further improve performance and efficiency.
- Further Memory Improvements: Enhanced memory bandwidth and capacity are likely to be key improvements.
- Increased AI Capabilities: These processors are likely to push the boundaries of AI processing even further.
The exact specifications and release dates remain shrouded in mystery, but these processors promise a continuous evolution in data center capabilities.
The Impact on Data Centers: A Revolution in the Making?
Nvidia's advancements aren't just incremental improvements; they represent a paradigm shift in data center architecture. The combination of optimized CPUs and GPUs, coupled with cutting-edge interconnect technologies, is poised to dramatically improve performance, efficiency, and scalability. This leads to:
- Faster AI Model Training: Accelerated development and deployment of AI solutions.
- Improved HPC Performance: Faster simulations and scientific discoveries.
- Enhanced Cloud Computing Capabilities: More powerful and responsive cloud services.
- Reduced Energy Consumption: Optimized architectures lead to potentially lower energy consumption, benefiting both the environment and operational costs.
Whether or not it's a complete "revolution" remains to be seen, but Nvidia’s innovations are undeniably significant. The future of data centers is looking incredibly powerful, efficient, and AI-driven.
Conclusion: The Future is Now
Nvidia's continued innovations in CPU and GPU technology, especially with Hopper, Grace, Rubin, and Feynman, are reshaping the landscape of data centers. This is not just about faster processing speeds; it's about enabling new possibilities in AI, HPC, and cloud computing. The coming years will undoubtedly witness a dramatic transformation in data center capabilities, driven by these exciting technological advancements. Stay tuned for further updates as more details about "Rubin" and "Feynman" emerge.